An Intro to Public Sector Capability Frameworks
Public sector capability frameworks are well-oiled machines, and they’re more important than you might think.
Most public sector departments, agencies and organisations work within a capability framework that define the transferable knowledge, skills and abilities relevant to their job roles or job levels.
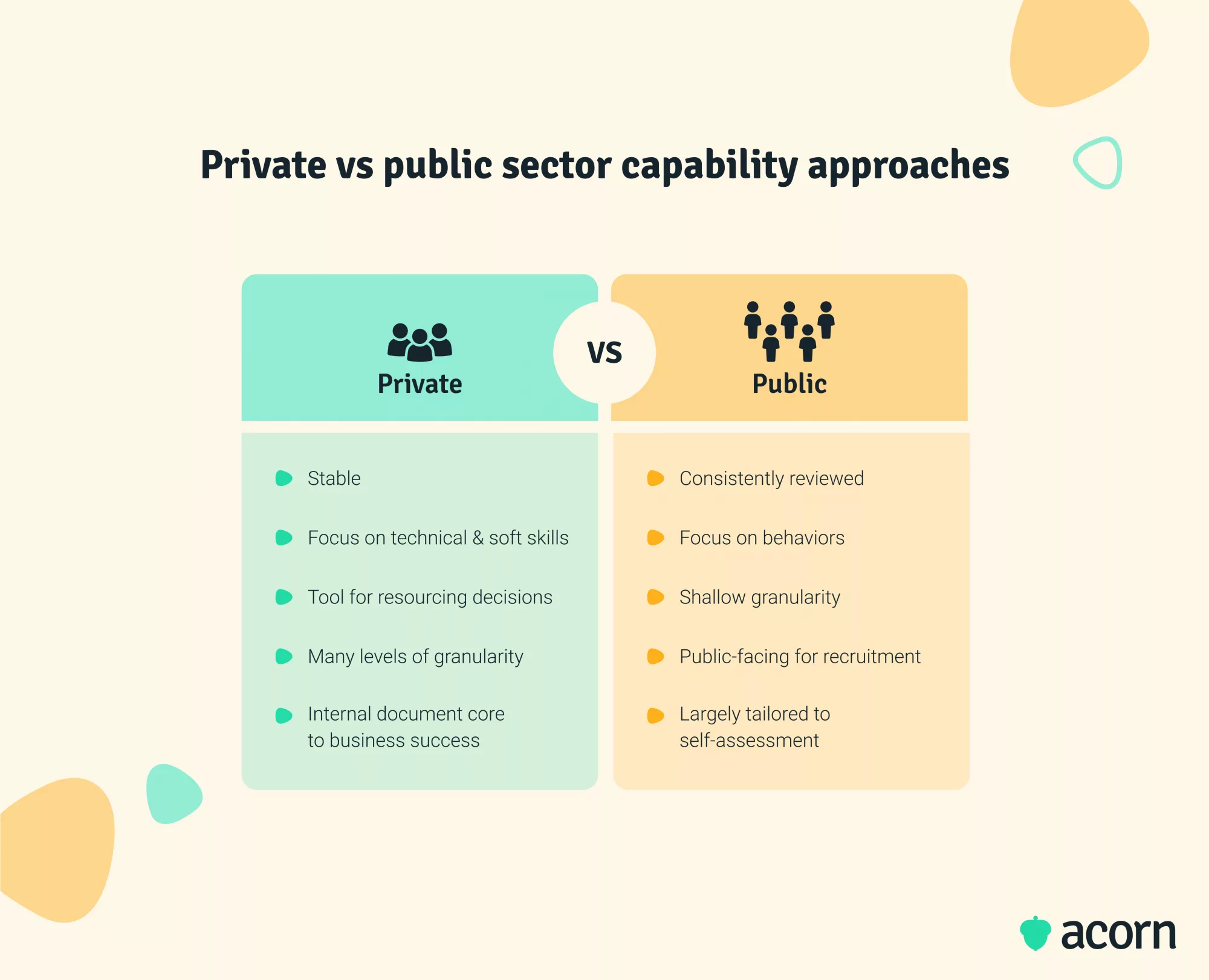
These differ from the frameworks you see in the private sector in a few ways. First on the level of granularity, second, how they emphasise behaviours above all else, and third, their purpose.
But before we dive deep, let’s look at just what a public sector capability (PSC) framework is and why it’s structured differently to private models.
What is a public sector capability framework?
A public sector capability framework outlines the knowledge, skills and behaviours or attributes required by those working in a public service or enterprise. These combined capabilities are defined by behavioural indicators considered necessary to achieve the objectives of a department now and into the future and ultimately benefit private citizens.
Why is a capability framework important for public sector?
If you’re familiar with frameworks used in private organisations, you’ll find that their public sector counterparts are a little different.
The major difference is the purpose for utilising one: PSC frameworks are formulated and reviewed in the interests of not just employees and the sector, but also the community they serve.
Public agencies, departments and organisations are responsible for vital everyday services. This can include (but of course isn’t limited to) education, health, legislation and social services. Each has everyday impacts on community, making it important for these functions to be based on the solid foundation of a highly capable, responsive and fit-for-purpose workforce.
This isn’t to say that PSC frameworks aren’t designed for the domains of employee performance, strategy or leadership development. These tenets do exist in most, if not all, public sectors as key to organisational success. The skills, behaviours and expertise required to reach organisational goals and fulfil a certain role are still a core part of the public sector capability framework, though the application of them is a little different.
Why PSC frameworks need to be agile
We know that private sector capability frameworks are designed to be stable as they often define what an organisation does well, thereby laying a pathway to future and potentially greater success. This is because the private sector is largely accountable to themselves.
But what affects the community is ever evolving (like each new variant of Covid), which means that the capabilities required by a workforce need to:
- Be viewed in the interest of developing employees as highly skilled, diverse and capable for the benefit of the public.
- Describe whole-of-sector expectations as much as a singular agency or department’s needs.
- Respond to cultural, social, environmental, and economic changes.
PSC frameworks must respond to current and future changes that may not be immediately predictable. This is why capability reviews are known to happen every few years—and considered as crucial a part of the process as creating the framework itself.